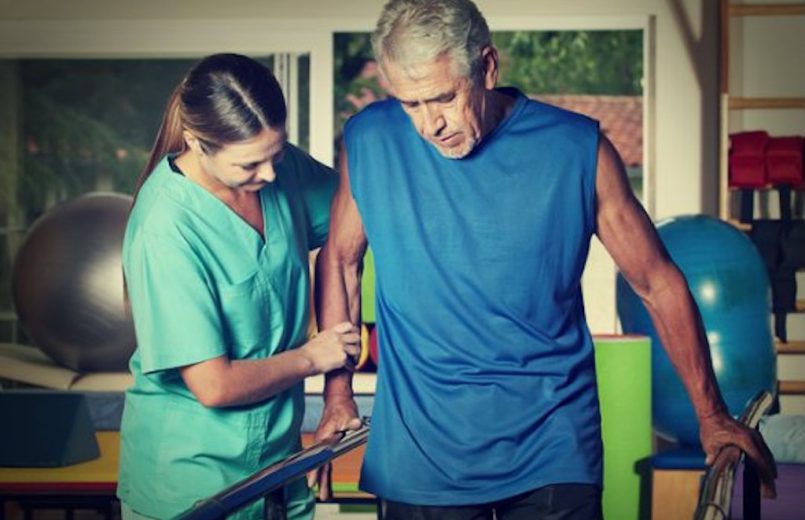
With physiotherapy in Dwarka, it is intended a total functional recovery of the operated knee, which allows the patient’s global re-education and the return of his level of activity and functionality after performing knee arthroplasty.
Total knee replacement in Delhi, that is, the surgery that replaces this joint with a knee prosthesis, is the final solution for many patients and has a high success rate.
Degenerative joint disease at the knee, called knee arthrosis or gonarthrosis, is a very common joint pathology that often affects the patient’s health and well-being. As the osteoarthritis of the knee progresses, it becomes impossible for the patient to carry out his daily activities properly, whether due to pain or to the mobility deficit that originates.
Can Physiotherapy be started before surgery?
If he so wishes, the orthopaedic in Dwarka sends the patient for observation and guidance by the physiotherapist in Dwarka, so that the patient starts the appropriate Physiotherapy even before the surgery. The beginning of the rehabilitation program in the preoperative phase is ideal for many patients with gonarthrosis.
In order to establish the Physiotherapy program, it is very important that the Physiatrist knows all the patient’s diseases and evaluates possible pathologies in terms of other joints, in addition to knee arthrosis to be operated on. It is necessary to objectify the articular amplitudes of this knee, the type and degree of its deformities and also the state of the thigh muscles (especially the quadriceps). Deficits in the patient’s functionality should also be assessed. The other knee and the two hips are also the focus of special attention, as well as the patient’s gait pattern.
And after surgery, when should Physiotherapy start?
After knee arthroplasty, the Orthopedic in Delhi sends all the relevant surgical information to the physiotherapist in Janakpuri, and the close collaboration between these two Medical Specialties is essential to obtain the best results. The rehabilitation of a patient who has undergone not only the placement of a knee prosthesis but the total reconstruction of this joint, which also includes soft tissue surgery (ligaments, tendons, joint capsules) will be scheduled. This aspect is particularly important when before surgery there was a significant deficit in knee extension and/or joint deformity. The rehabilitation program is always adjusted to the reality of each patient.
The therapy should be initiated immediately on the day following knee arthroplasty, while the patient is still in the hospital. When the patient is discharged from the hospital and returns to his home, the continuation of the physiatric treatment should be scheduled immediately.
Objectives of physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in Janakpuri aims to fully recover the function of the operated knee, allowing the patient’s global re-education and the resumption of their level of activity and functionality.
It is often necessary to carry out muscle-strengthening work on the two upper limbs and the non-operated lower limb so that the activities of daily living are carried out with greater safety and that progress can be made more quickly in the rehabilitation program.
The most specific rehabilitation work at the level of the operated lower limb includes:
- control of pain and edema;
- gain in knee joint amplitudes (extension and flexion);
- gain in overall muscle strength, especially at the quad-level;
- gain of flexibility;
- balance gain;
- re-learning the correct gait pattern.
The knee flexion so that the patient can comfortably sit in a chair should be around 90º and to get up from the chair it should be around 105º.
During the evolution of arthroscopic changes in the knee joint, the quadriceps, muscle of the anterior aspect of the thigh (front), also undergoes changes. The decrease in the activity of this muscle causes it to become progressively hypotonic (“weak”). After knee prosthesis surgery, the atrophy of the quadriceps muscle increases and its contraction capacity decreases, also due to neuro-reflex inhibition of this muscle by surgical intervention in the joint. Post-operative exercises to strengthen the quadriceps should then be started as soon as possible.
The evolution of knee arthrosis also causes a shortening of the soft structures of the posterior region of the knee, namely of the ischio-tibial muscles, so the flexibility exercises of these structures are essential.
The re-education of the gait pattern is a very important facet of the rehabilitation program, and, if it is not carried out soon after the surgery, it can imply an alteration of the global posture and insecurity in walking.
The risks and complications of physical therapy are rare. It is always necessary to keep a close watch on the skin and inflammatory signs.
What does physiotherapy consist of?
Physiotherapy after knee prosthesis surgery is done through a set of techniques and methods that speed up and optimize the patient’s recovery so that the maximum performance of this surgery can be removed.
During the entire rehabilitation process after knee arthroplasty, it is necessary to frequently evaluate the results obtained and the proposed objectives, since it is often necessary to adjust these objectives and alter the treatment, depending on how each patient is evolving. The internationally accepted and instituted rehabilitation protocols are fundamental as guidelines, but it is the knee and the patient that was operated on that impose the evolution of the Physiotherapy program, that is, the passage or not to the next phase of the protocol.
Right after surgery
In the immediate postoperative period, it is very important to teach the patient and his family how to get out of bed, get up, sit and move to a chair, as well as the correct way to walk, always with the help of a walker.
Adequate exercises for mobilizing the knee and the remaining lower limbs and also for muscle strengthening must be initiated, namely the quadriceps and hip extensors.
When the orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi understands this and following his instructions, continuous passive knee mobilization with an arthrometer device is included in the treatment, which is usually only performed while the patient is hospitalized.
The patient and family should also be taught not to place a pillow behind the operated knee when lying down, but under the heel, in order to achieve complete knee extension. Another very important aspect is the teaching of techniques that protect the operated knee, such as on the stairs, where the operated lower limb must be the first one when descending and the reverse must be done when climbing.
The application of static ice is indicated for the control of inflammatory signs, and should not exceed 12 minutes. Dynamic ice (continuous movement of an ice cube in the region) is an excellent option.
After hospital discharge
If possible, part of the rehabilitation program should be carried out in the form of hydrotherapy.
When the orthopedic in Dwarka understands that the patient can now start using only one Canadian in walking, it is essential to train the patient for this situation.
The neuro-muscular reeducation of the quadriceps is essential for the gait to have controlled knee flexion in the support phase, making it safer.
The balance and proprioception training (awareness of position) of the knee allows a faster adaptation to the prosthesis.
Walking backward or moving the bicycle pedals backward are important exercises, especially in cases where there is a deficit in knee extension.
The final phase of the rehabilitation program is the reconditioning of the effort (cardiovascular training) and the training of playful and / or sporting activities, aiming at resuming or even improving the patient’s level of functionality.
Home rehabilitation
At home, after each Physiotherapy session, the patient should pay attention to aspects previously mentioned, such as the posture of the lower limb in extension (without a pillow behind the knee) and the correct way of going up and downstairs.
Muscle-strengthening exercises that were taught to be performed at home should also be performed according to the instructions. As long as you feel pain or edema (“swelling”), you can apply ice, always with care.
After physiotherapy, that is, after the rehabilitation program at the hospital or physiotherapy clinic in Dwarka has ended, the patient must maintain the specific exercises indicated, especially for strengthening the quadriceps muscle and flexibility.
Physical activity
Physical activity should be appropriate to the patient’s cardiovascular taste and condition.
The exercise should always increase very gradually in time and intensity. In general, high impact exercises on the knee should be avoided.
Walking is one of the most recommended exercises, as well as exercise bikes, swimming and golf.