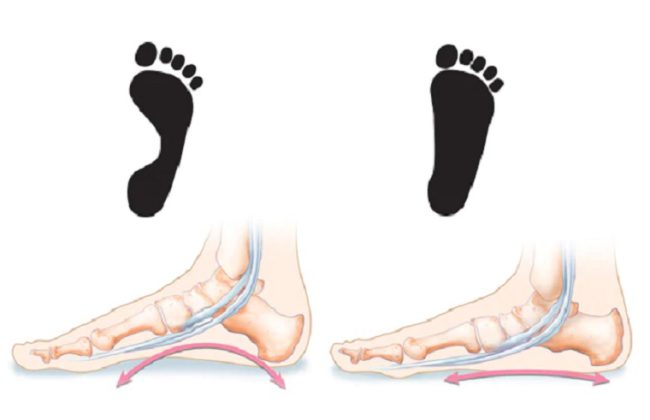
Flat foot is a common condition. It is normal in babies and young children. Flat feet occur because the tissues that support the joints in the foot (called tendons) are loose.
Orthopaedic Treatment
The orthopaedic in Delhi will indicate the use of insoles in order to try to originate the plantar arch in a physiological way. It will also suggest the use of wide footwear in the forefoot with a posterior buttress that supports the calcaneus; that it has a sole but hard or fine rubber; laces or adjustment straps; with slightly raised heel, with internal wedges as appropriate. In many cases, they do not need to boot, but it is advisable to place them preventively on the child who begins to walk. Corrective insoles are placed from 2 years of age; Depending on the construction material, they can be of the soft, semi-rigid or rigid type, depending on the age and the correction required. Their change depends on the growth of the foot and, as a rule, they must be changed annually.
Physiotherapy treatment
In conjunction with orthopaedic treatment, exercises will be performed, in cycles and repetitions that will depend on the tolerance of the patient, which will be aimed at strengthening the muscles involved to stimulate the formation of the plantar arch. Among the suggested exercises physiotherapist in Dwarka can mention:
- Walk on tiptoe from one end to the other, either on the floor or on carpets with different textures to activate proprioceptive work.
- Try to grab small objects with your toes. (laymen, colors, small balls), after mastering the grip, you can start moving from one side to the other with the objects.
- March with the outer edge of the feet and on the heels
- When standing on the edge of a step, gently drop your heels back to lengthen the achilles tendon.
- Lower limb muscle stretching
- Reeducation and coordination of the march
In addition to the exercises, physical agents will also be used to prepare the muscles to work, also including superficial and deep myofascial inductions to release the compromised tissue.
Surgical treatment
This is a surgical intervention as there is no improvement with rehabilitation and orthopedic treatment. Being flat feet candidates irreducible valgus with anomalies in the means of joint connection, or vertical talus; likewise in the case of presenting antalgic gait due to insufficiency of the posterior tibial tendon, post traumatic, instability of the foot-ankle joints, etc.
The principles of surgical treatment are:
- Transplantation of another tendon to aid the function of the posterior tibial tendon (usually the long flexor is transplanted from the big toe)
- Restoring the shape and alignment of the foot. This realigns the load to the center of the ankle.
Possible complications of surgical treatment
- Wound healing problems
- Infection
- Failure to heal bone (non-union) that has been cut or joints that have joined
- Deep venous thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Neurological injury
- Vascular injury
- Pain and deformity continue
Recovery from surgery depends on the particular combination of procedures that are performed. However, if bone cutting and repositioning or joint fusion is required (typically required) a typical recovery would take 4-6 months to achieve much of the recovery, and 12-18 months prior that they reach their point of maximum improvement.
It is recommended that surgical treatments be the last option.